What is the conditions for obtaining Highly Skilled Professional visa? Explanation of “point system,” “preferential treatment,” and ” the differences between No.1 and No.2″

A Highly Skilled Professional visa has advantages such as relaxation of Permanent Resident requirements and the ability to bring a parent.
On this page, we will explain the conditions for obtaining a Highly Skilled Professional visa and preferential treatment.
Index
1. What is a Highly Skilled Professional visa?
1-1. What is a Highly Skilled Professional visa?
Highly Skilled Professional visas were established in 2015 to promote the acceptance of foreigners with advanced abilities and qualities (highly skilled personnel) who are expected to contribute to economic growth and the creation of new demand and employment.
In order to actively accept highly skilled personnel, Highly Skilled Professional visas are granted with a period of stay of “5 years” (“Indefinite period” for Highly Skilled Professional visa (No.2) and multiple residence activities, and other preferential treatment.
In addition, entry and residence procedures for Highly Skilled Professional visas are processed preferentially, which is also beneficial for the accepting company.
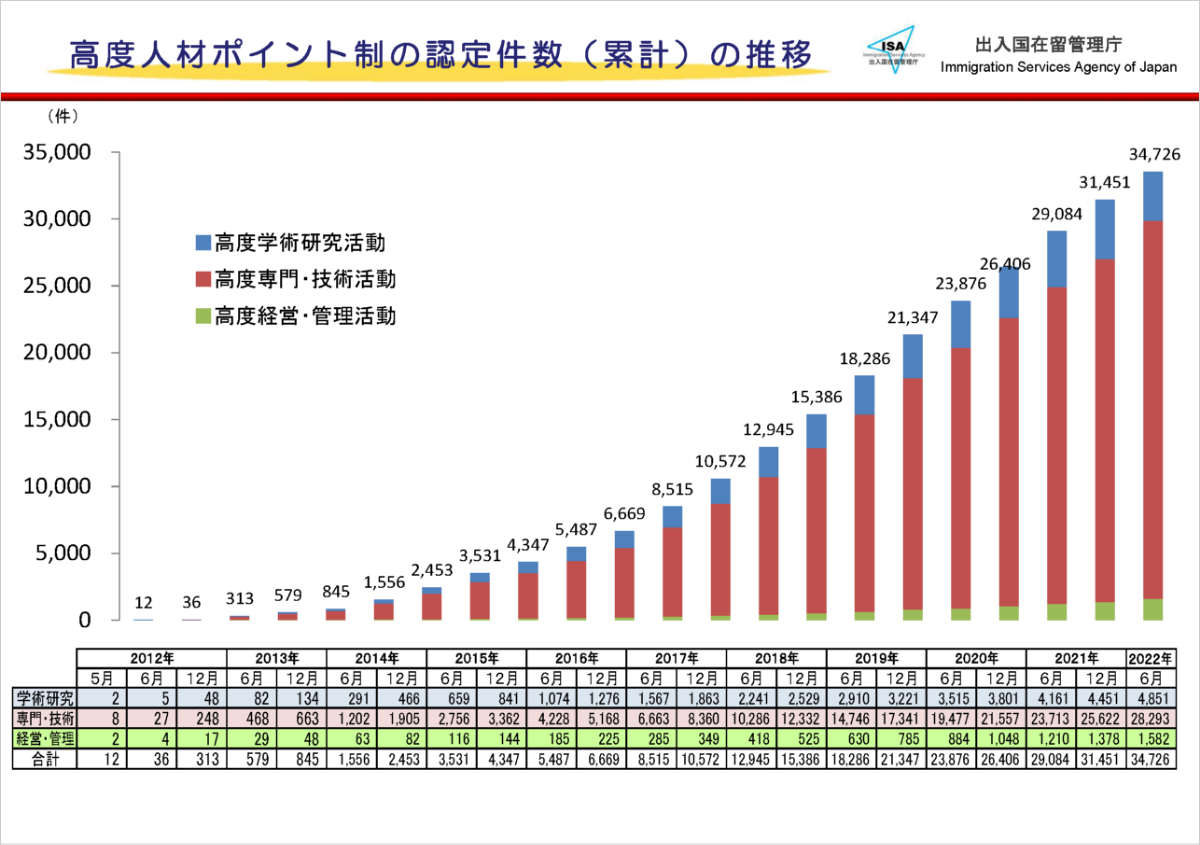
See the table below.
According to the press release released by the Immigration Services Agency, as of the end of June 2022, 34,726 foreigners are said to be residing in Japan with Highly Skilled Professional visa.
It is no exaggeration to say that the trend in the number of foreigners holding Highly Skilled Professional visas are a notable indicator from the perspective of Japan’s economic development.
1-2. Highly Skilled Professional No.1
Highly-skilled professional visas are roughly divided into “Highly-skilled Professional No. 1” and “Highly-skilled Professional No. 2.”
Highly Skilled Professional No. 1 is further classified into (a), (b), and (c) according to the content of their activities.
The occupations and specific examples that fall under Highly Skilled Professional No. 1 are as follows.
This is called advanced academic research, and includes research, research guidance, and educational activities based on contracts with public institutions and private companies in Japan.
Specifically, this includes educational activities at educational institutions such as universities, and research activities at research institutes of private companies.
In addition to these activities, it is also possible to launch a related business and manage it yourself by making use of the results of education and research.
It is called advanced specialization and technology, and corresponds to activities that engage in work that requires knowledge or skills in the fields of natural sciences or humanities based on contracts with Japanese public institutions or private companies.
Specifically, this includes professional occupations such as activities to engage in product development work as an engineer, planning work, and activities as an IT engineer at the company they belong to.
In addition to these activities, it is also possible to launch a related business and manage the business yourself.
There are many overlaps with the activities of the Engineer/Specialist in Humanities/International Services visa, but please note that the activities that fall under International Services on the Engineer/Specialist in Humanities/International Services visa do not fall under Highly Professional No. 1 (b). is.
It is called advanced management and administration, and corresponds to activities to manage or administer businesses in Japanese public institutions and private companies.
Specifically, this includes the management of companies, as well as the management and administration of law offices and tax accountant offices.
In addition, in conjunction with these activities, it is also possible to launch a company or office related to the activity content and run the business yourself.
As mentioned above, the Highly Skilled Professional No. 1 is different from other visas in that multiple activities are permitted.
In addition, the maximum period of stay under the current system, 5 years, will be uniformly granted.
This is also an advantage for companies that employ highly skilled foreign personnel in a stable manner.
1-3. Highly Skilled Professional No.2
Highly Skilled Professional No. 2 is for those who have been working as Highly Professional No. 1 for 3 years or more.
Almost all employment activities can be carried out in conjunction with the activities of Highly Skilled Professional No. 1.
Specifically, you can engage in any of the Highly Skilled Professional No. 1 (a), (b), or (c) activities, or in conjunction with these activities, the activities permitted by the following visas.
* “Professor”, “Art”, “Religion”, “News”, “Legal/Accounting Services”, “Medical Care”, “Education”, “Engineer/Specialist in Humanities/International Services”, “Nursing Care”, “Entertainer”, Activities corresponding to “Skilled Worker” and “Specified Skilled Worker No. 2” visas.
The period of stay for the Highly Skilled Professional No. 2 visa is “indefinite” as long as the person is engaged in activities that fall under the Highly Skilled Professional visa.
In addition, it is characterized by the fact that activities can span multiple visas.
1-4. Differences between Highly Skilled Professional Visa No. 1 and No. 2
In the case of Highly Skilled Professional No. 1, the period of stay is 5 years.
On the other hand, the period of stay for Highly Skilled Professional No.2 is “indefinite.”
As a result of the indefinite period of stay, it is no longer necessary to obtain permission to extend the period of stay.
In addition, in the case of Highly Skilled Professional No.1, in addition to their main activities, they are permitted to carry out their own business management activities related to this.
On the other hand, in the case of a Highly Skilled Professional No.2, the scope of activities will be further expanded, and in addition to the main activities, almost all activities permitted by other work visas will be possible.
2. What is the point system for the Highly Skilled Professional visa?
As a condition for obtaining a Highly Skilled Professional visa, it is necessary to engage in activities corresponding to Highly Skilled Professional No.1 or No.2.
In addition, it is necessary to clear a certain number of points by “point calculation”.
This is called the “Highly Skilled Professional Point System.”
The point system for highly skilled personnel is a system that gives preferential treatment to particularly outstanding foreign nationals who can obtain work visas.
Among the foreign nationals who are eligible for a work visa, points are given for each item such as academic background, work history, annual income, Japanese language ability, etc., and those who achieve a total of 70 points or more are recognized as highly skilled personnel. You will be granted a Highly skilled Professional visa.
In addition, it is not required to maintain a score of 70 or higher at all times during the period of stay as a highly skilled personnel.
However, it should be noted that if the total points are less than 70 points at the time of application for permission to extend the period of stay, permission to extend the period of stay for a Highly Skilled Professional visa can not be obtained.
3. Let’s actually calculate points for a Highly Skilled Professional visa!
Below is an overview of the point calculation table published by the Immigration Services Agency.
The point calculation table consists of items such as educational background, work experience, annual income, age, research achievements, qualifications, and special additions, and points are assigned to each item.
Let’s actually calculate using the point calculation table.
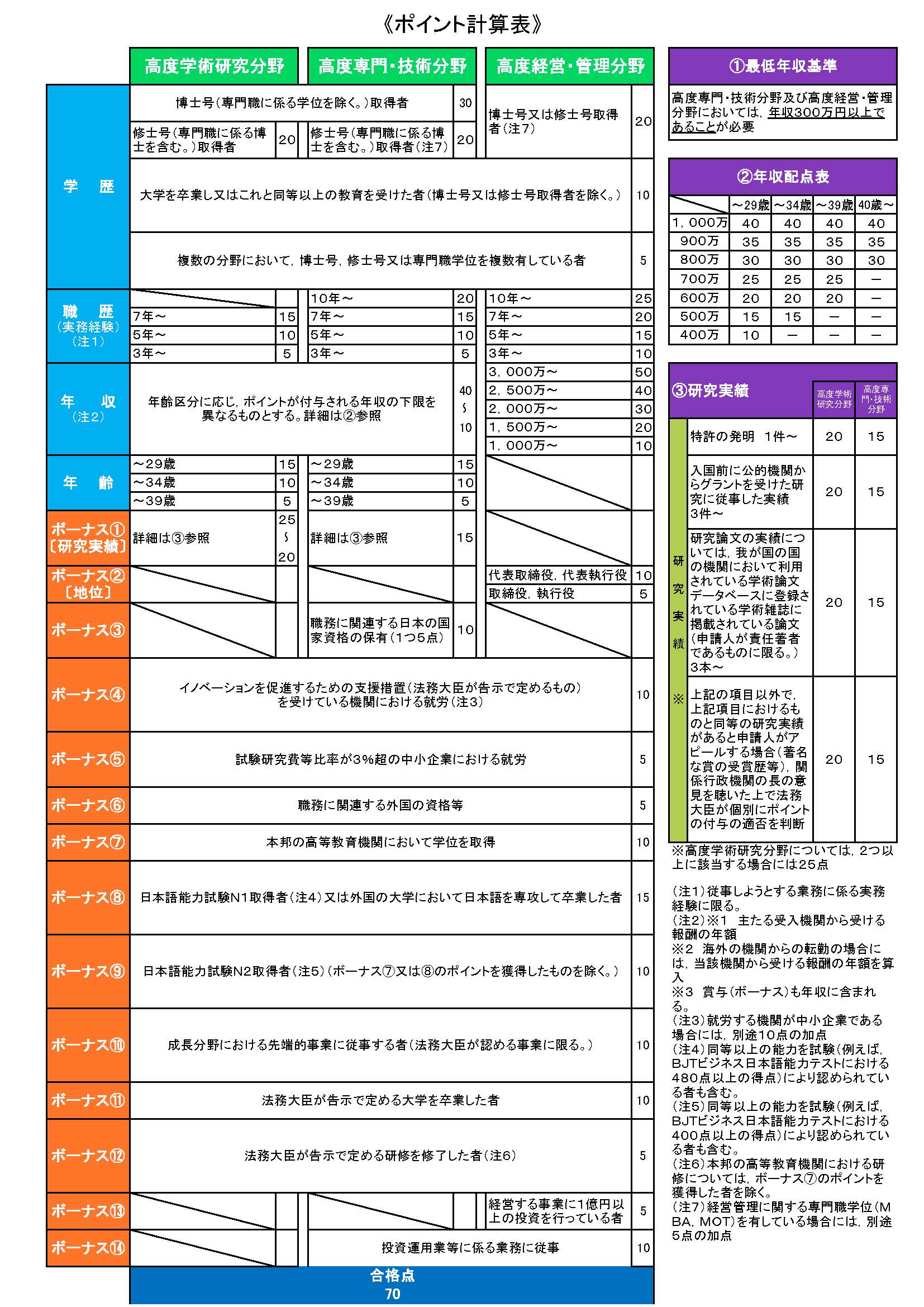
Below is a supplementary explanation of each item in the point calculation table.
“University” includes junior colleges.
Those who have graduated from a college of technology or those who have graduated from a specialized course at a vocational school (“Advanced Diploma”) are treated as “persons who have received an education equivalent to or higher than that of a university” and are eligible for academic background points.
On the other hand, those who have completed a specialized course at a vocational school and received the title of “Diploma” are not eligible for academic background points.
Only the number of years of practical experience in the work you are engaged in is recognized as work history.
If you wish to obtain a Highly Skilled Professional No. 1(b) (highly skilled professional/technician), Highly Skilled Professional No. 1(c) (highly skilled management/administration), or a Highly Skilled Professional visa for the equivalent High Skilled Professional No. 2 must have an annual income of 3 million yen or more.
Even if the total points calculated for points other than annual income reaches 70 points or more, if the annual income is less than 3 million yen, it does not meet the requirements for a Highly Skilled Professional visa.
In addition, the annual income in the point calculation table does not mean the annual income in the past, but the annual income expected to be obtained from activities with a Highly Skilled Professional visa.
In addition to basic salary, bonuses, diligence allowances, adjustment allowances, etc. are included, but commuting allowances, dependent allowances, housing allowances, etc., which have the nature of reimbursement for actual expenses (excluding those subject to taxation) are NOT included.
Overtime pay is not included in the annual income of the point calculation table because it is paid based on the actual overtime work.
* Fixed overtime pay (fixed overtime pay) is included in the annual income of the point calculation table because it is overtime pay that pays a fixed amount of extra wages in advance regardless of whether or not there is overtime.
Being young does not indicate the abilities and qualities of a highly skilled foreign personnel, but Japanese companies still have a seniority-based wage system, making it difficult for young people to earn a high income.
As a result, it becomes difficult to expect high scores in terms of annual income points, and as a result, being young is a disadvantage, so points are given according to age to compensate for this.
Points will be awarded based on certain research achievements, such as having 1 or more patented inventions as an inventor, 3 or more treatises published in academic journals listed in the academic paper database.
It is necessary to have a Japanese national qualification (business monopoly qualification or name monopoly qualification) related to the work to be engaged.
Therefore, possession of a private qualification does not fall under this category.
As a comparison, exams and qualifications related to information processing technology listed in so-called IT notices are also covered.
Regarding the special addition items, we will explain the items that are frequently inquired about in practice and the financial human resources newly added to the special addition items.
First, points are awarded by graduating from a Japanese university or completing a graduate school course. In addition, points will be awarded for those who have graduated from a foreign university majoring in Japanese or have passed N2 of the Japanese Language Proficiency Test.
Therefore, if you graduated from a Japanese-language university and passed N1, you are very close to obtaining a Highly Skilled Professional visa.
Next, points will be added for those who have graduated from the following universities published by the Immigration Services Agency.
- List of universities eligible for additional points based on the World University Rankings
- Top Global University Creation Support Project
- Universities designated as “partner schools” in the Innovative Asia Project implemented by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs
Finally, among highly skilled foreign personnel engaged in Highly Skilled Professional No. 1-B (Highly Skilled Professional/Technical Skill) and Highly Skilled Professional No. 1-C (Highly Skilled Management/Administration) Those engaged in investment advisory/agency business or investment management business are newly eligible for special points system for highly skilled personnel.
4. Seven Preferential Treatments for Highly Skilled Professional Visa
4-1. Relaxation of Permanent Resident Permit Requirements
In order to receive permission for Permanent Resident, as a general rule, it is necessary to have lived in Japan continuously for at least 10 years.
Highly skilled foreign personnel with a score of 70 or higher on the point calculation table will be granted permission to Permanent Resident in Japan after 3 years, and those with a score of 80 or higher will be granted permission to after 1 year.
It can be said that the relaxation of the requirements for permission for Permanent Resident will be a great advantage for those who are aiming for a Highly Skilled Professional visa.
>> Click here for highly skilled personnel Permanent Resident visa
4-2. Allowing Parent to Accompany
Under the Immigration Control Act, there are no visas other than the Highly Skilled Professional visa.
Some are acceptable for humanitarian reasons, but the practical requirements are very strict.
>>Click here for Designated Activities visa(Elderly parent support)
However, when raising a child under the age of seven of a highly skilled foreign personnel or his/her spouse, the parent of the highly skilled foreign personnel or his/her spouse can be brought to Japan.
It says that this is a reason for many people to aim for a Highly Skilled Professional visa.
If there are two points to note, (1) it is only possible for highly skilled foreign personnel to be invited by their parents if their annual household income is 8 million yen or more, (2) please be aware that this is limited to one parent of the highly skilled foreign personnel or spouse.
4-3. Allowing domestic servant to accompany
If a highly skilled foreign personnel has an annual household income of 10 million yen or more, under certain conditions, he/she can continue to employ a domestic servant who was employed overseas and accompany him/her to Japan.
In addition, if the spouse is unable to engage in daily housework due to illness, etc., or if there are children under the age of 13, it is possible to hire new domestic servant after entering the country and invite them from overseas.
Furthermore, highly skilled foreign personnel engaged in the investment management industry, etc., can hire new domestic servant after entering Japan under certain conditions and invite them from overseas.
4-4. Grant of period of stay “5 years”
Highly Skilled Professional No. 1 is granted a uniform period of stay of 5 years, which is the longest period of stay under the Immigration Control Act.
4-5. Spouse’s employment
The spouse of a person staying in Japan on a work visa can stay in Japan on a family visa and work with permission to engage in activity other than that permitted under the status of residence previously granted.
However, in that case, there is a time limit of 28 hours or less per week.
On the other hand, if the spouse of a person staying in Japan on a Highly Skilled Professional visa is engaged in work activities that fall under the category of “Research”, “Education”, “Engineer/Specialist in Humanities/International Services”, or a part of the “Entertainer” visa, You can work without time limits.
4-6. Permitting multiple residence activities
Other working visas only allow activities within the scope of the permitted visa, and if you want to conduct business outside the scope of the permitted visa, you must obtain permission to engage in activity other than that permitted under the status of residence previously granted.
However, those staying in Japan on a Highly Skilled Professional visa are permitted to engage in related business management activities in addition to their main activities.
4-7. Priority processing for immigration and residence procedures
Entry and residence examinations for highly skilled foreign personnel are processed prior to foreigners with other visas.
Specifically, an application for a certificate of eligibility will be processed within 10 days of receipt of the application, and an application for permission to extend the period of stay and an application for permission to change the status of residence will be processed within 5 days of receipt of the application.
5. Highly Skilled Professional visa case study
In order to get a concrete image, we would like to apply the point calculation table based on a case study and consider whether or not you meet the requirements for a Highly Skilled Professional visa.
Mr. A (29 years old), who is of Chinese nationality, graduated from the Faculty of Commerce at a Japanese university and got a job at the current food manufacturer at the age of 23. Since joining the company, he has been involved in marketing operations and has 5 years and 6 months of practical experience. Annual income for the next year is expected to be 4.8 million yen. In addition, Mr. A passed the Japanese Language Proficiency Test N1 while he was in university.
Mr. A wishes to change from his current Engineer/Specialist in Humanities/International Services visa to Highly Skilled Professional No. 1-b (Highly Specialized/Engineer).
【Examination】
Apply it to the point table, points will be given for the following items.
Academic Background: Graduated from university (10 points)
Work experience: 5 years or more and less than 7 years (10 points)
Annual Income: Under 30 years old, 4-5 million yen (10 points)
Age: Under 30 (15 points)
Special addition: graduated from a Japanese university (10 points), passed the Japanese Language Proficiency Test N1 (15 points)
As a result of point calculation, Mr. A’s total points reached 70 points.
* If the university that Mr. A graduated from is listed in the above list of universities eligible for additional points, an additional 10 points will be added.
Mr. B (36 years old), who has German nationality, majored in Japanese literature at a graduate school in Germany and obtained a master’s degree. (The graduate school that Mr. B graduated from is listed in the graduate schools eligible for addition.)After that, He came to Japan and studied advertising design production and copywriting for 2 years at a vocational school. After graduating from a vocational school, he got a job at an advertising agency, and after changing jobs twice, he is working at his current company. All the companies that Mr. B has worked for so far have been advertising agencies, and all the work he has been related to advertising production. He has 6 and a half years of work experience. Annual income for the next year is expected to be 6.5 million yen. In addition, Mr.B passed the Japanese Language Proficiency Test N2 while he was in college.
Mr. B wishes to change from his current Engineer/Specialist in Humanities/International Services visa to Highly Skilled Professional No. 1-b (Highly Specialized/Engineer).
【Examination】
Apply it to the point table, points will be given for the following items.
Academic background: Master’s degree at graduate school (20 points)
Work experience: 5 years or more and less than 7 years (10 points)
Annual income: 35-39 years old, 6-7 million yen (20 points)
Age: 35 to 39 years old (5 points)
Special addition: Passed N2 of the Japanese Language Proficiency Test (10 points)
Special addition: Graduated from a graduate school eligible for addition based on the World University Rankings (10 points)
As a result of the point calculation, Mr. B’s total points reached 70 points.
* Employment history does not mean work experience in the same industry or at the same company. It will be possible to count as work experience if the work you have engaged in is the same. Even if Mr. B has changed jobs several times, in cases where he is consistently engaged in the same work, each period of work is counted as work experience.
Mr. C (age 30), who has Korean nationality, majored in economics and obtained a bachelor’s degree from a Japanese university (the university Mr. C graduated from is listed in the universities eligible for addition). Immediately after graduating from university, Mr. C established a company and assumed the post of CEO. After that, he obtained a Business Manager visa and has been running a trading company for 6 years. Mr. C’s executive compensation for the next year is 3.6 million yen. Mr. C’s company is run by Mr. C, the representative, and two Japanese part-time staff. In addition, Ms. C passed the Japanese Language Proficiency Test N1 while he was in college.
Mr. C wishes to change his current Business Manager visa to Highly Skilled Professional No. 1 c (advanced business manager).
【Examination】
Apply it to the point table, points will be given for the following items.
Academic Background: Graduated from university (10 points)
Work experience: 5 years or more and less than 7 years (15 points)
Position: Representative Director (15 points)
Special addition: Graduated from a Japanese university (10 points)
Special addition: Passed N1 of the Japanese Language Proficiency Test (15 points)
Special addition: Graduated from a graduate school eligible for addition based on the World University Rankings (10 points)
As a result of the point calculation, Mr. C’s total points reached 70 points.
* Employment history refers to practical experience related to business management or administration.
In addition, Highly Skilled Professional No. 1 is divided into (a), (b), and (c), and in Mr. C’s case, the point calculation table corresponding to Highly Skilled Professional No. 1 (c) will be used for calculation.
When Mr. C got to consult with us, he was worried that the business scale and executive compensation were smaller than those of entrepreneurs who had started businesses at the same time. When we checked his career history, it was found that the total points exceeded 70 points.
If you prepare to start a business while you are an international student and meet the above requirements after graduation, you have a good chance of applying for a Highly Skilled Professional visa.
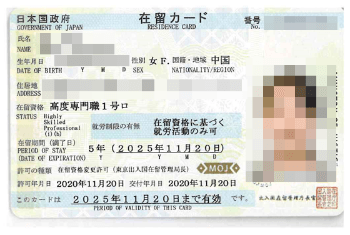
Here the image of the Residence Card is an example of the Highly Skilled Professional Visa obtained through us.
Many have obtained the Highly Skilled Professional Visa through us and are expanding their opportunities to contribute in Japan.





6. Summary of conditions for obtaining a Highly Skilled Professional visa
The Japanese government has established seven preferential treatment measures for Highly Skilled Professional visas in order to further promote their acceptance.
In addition, I have heard that in some cases bank loans and business loans will also be possible.
If you are considering continuing to live in Japan stably in the future and are considering obtaining a Highly Skilled Professional visa, what types of occupations and activities fall under the Highly Skilled Professional visa, whether the conditions for acquiring a Highly Skilled Professional visa are cleared or not by point calculation are two big keys.
Regarding these two points, it is often difficult for the foreigner himself or the person in charge of the company to make a judgment, so there are cases where we consult with us.
We are happy to answer any questions or provide consultations regarding Highly Skilled Professional visas free of charge.
Please feel free to contact us, Daiichi Sogo Office.